
Permalinks are the permanent URLs of your web pages and posts. They are one of the most important factors for SEO and user experience, as they tell search engines and visitors what your content is about, how it is organized, and how to access it.
However, sometimes you might need or want to change your permalinks, either intentionally or unintentionally. This can happen due to various reasons, such as human error, plugin updates, or server issues.
Changing permalinks can have a significant impact on your site, as it can cause a temporary drop in organic traffic and rankings. This happens because search engines and visitors might not be able to find your content under the new URLs, and you might lose the authority and trust that you have built with the old URLs.
But don’t panic! Changing permalinks can also be beneficial for your site in the long run, and the traffic loss can be embraced as a natural consequence of improving your site. In this article, we will show you how to assess the impact of the permalink change, how to recover from the traffic loss, and how to optimize the new permalinks for SEO and user experience.
How to assess the impact of the permalink change
The first step to deal with the permalink change is to understand how it affected your site. You can use various tools and methods to measure the date, magnitude, and sources of the traffic loss, as well as the keywords and pages that were most affected, and any technical issues or errors that might have occurred during the permalink change.
Google Analytics and Google Search Console
Google Analytics and Google Search Console are two of the most powerful and popular tools to monitor your site’s performance and health. You can use them to identify the date and magnitude of the traffic loss, as well as the sources of the traffic, such as organic, direct, referral, social, or email.
To do this, you need to compare the traffic data before and after the permalink change, and look for any significant changes or trends. For example, you can use the date range comparison feature in Google Analytics to see how the traffic changed over time, and use the acquisition reports to see how the traffic sources changed. You can also use the annotations feature to mark the date of the permalink change on the charts, so you can easily see the impact.
Similarly, you can use Google Search Console to see how the permalink change affected your organic traffic and rankings. You can use the performance report to see how the impressions, clicks, CTR, and positions changed over time, and use the filters to see the data by query, page, country, device, or search appearance. You can also use the coverage report to see how many pages were indexed and crawled by Google, and how many pages had errors or warnings.
Here are some examples of how to use Google Analytics and Google Search Console to assess the impact of the permalink change:
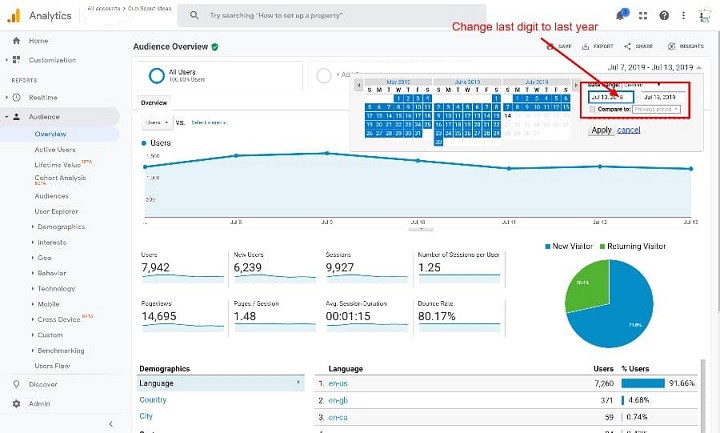
This screenshot shows the date range comparison feature in Google Analytics.
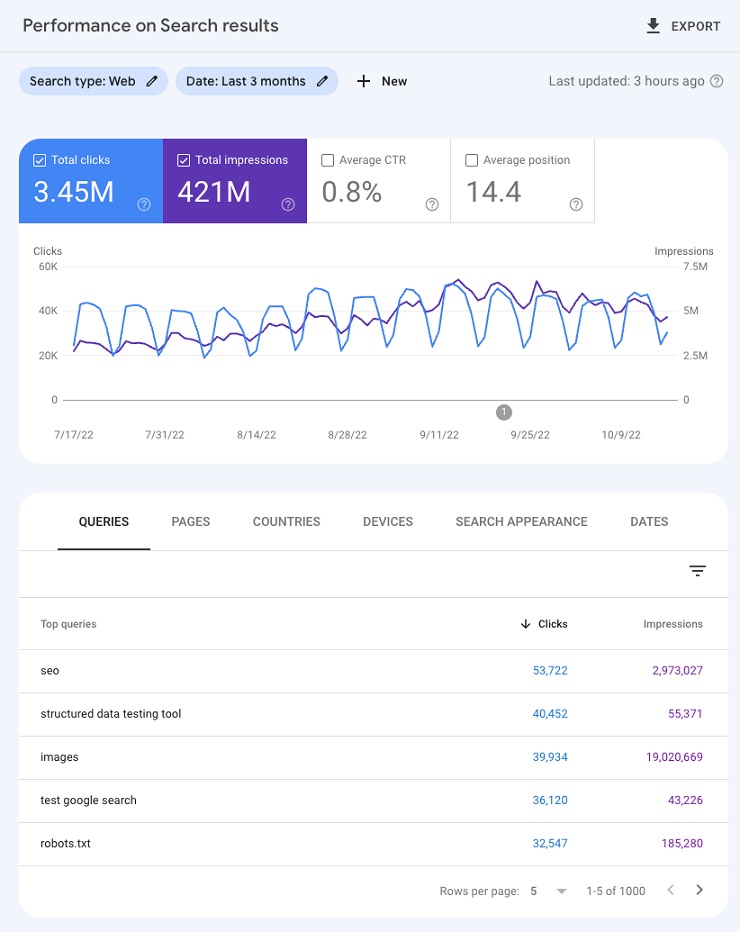
This screenshot shows the performance report in Google Search Console, showing the impressions, clicks, CTR, and positions for the site.
SEMrush
SEMrush is another powerful and popular tool to analyze your site’s SEO performance and health. You can use it to identify the keywords and pages that were most affected by the permalink change, and to see how your site’s visibility and authority changed in relation to your competitors.
To do this, you need to use the domain overview and the organic research features in SEMrush, and compare the data before and after the permalink change. You can also use the position tracking feature to track the rankings of your target keywords over time, and see how they changed after the permalink change.
Here are some examples of how to use SEMrush to assess the impact of the permalink change:
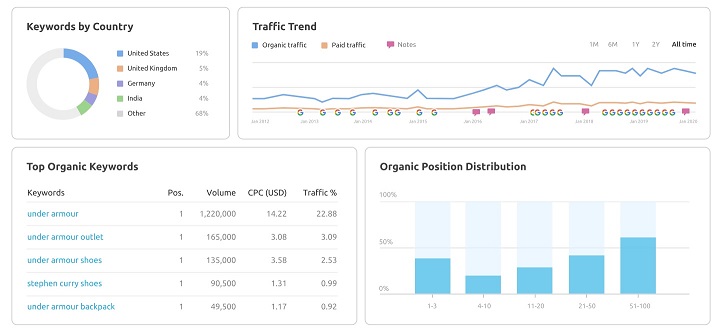
This screenshot shows the domain overview feature in SEMrush, showing the organic search, paid search, backlinks, and display advertising data for the site.
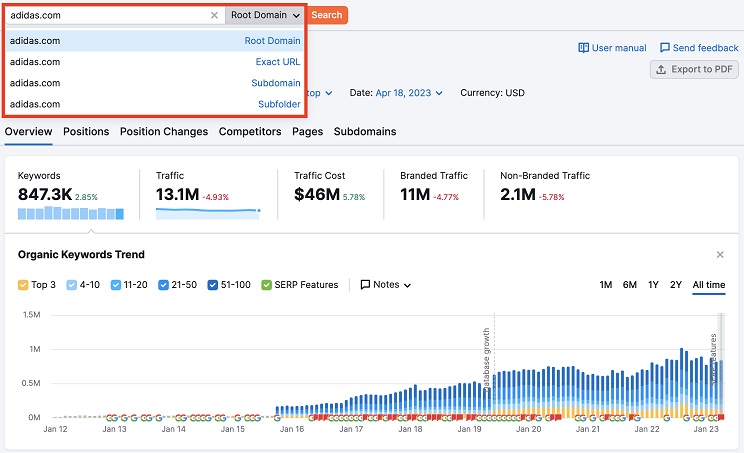
This screenshot shows the organic research feature in SEMrush.
Site crawler
A site crawler is a tool that crawls your site and analyzes its structure, content, and links. You can use it to identify any technical issues or errors that might have occurred during the permalink change, such as broken links, missing redirects, duplicate content, or canonical problems.
To do this, you need to run a site crawl before and after the permalink change, and compare the results. You can also use the site audit feature in some site crawlers to get a comprehensive report of your site’s health and performance, and to see the list of issues and recommendations to fix them.
Some of the most popular and reliable site crawlers are Screaming Frog, Sitebulb, and DeepCrawl. Here are some examples of how to use a site crawler to assess the impact of the permalink change:
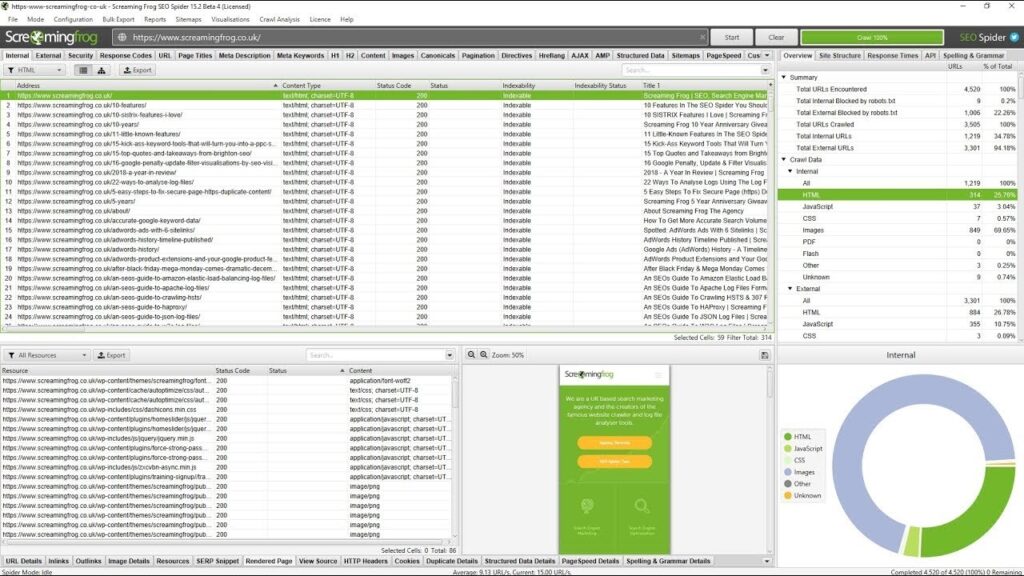
This screenshot shows the site crawl feature in Screaming Frog, showing the list of URLs, status codes, titles, and other data for the site before and after the permalink change. You can see that some of the URLs changed from 200 (OK) to 301 (Moved Permanently) or 404 (Not Found) after the permalink change, indicating that some of the pages were redirected or deleted.
How to recover from the traffic loss
The next step to deal with the permalink change is to recover from the traffic loss and restore your site’s performance and health. You can use various strategies and methods to fix any technical issues or errors that were identified in the previous section, and to ensure that the new permalinks are properly indexed and crawled by search engines. You can also use various techniques and tools to update any internal and external links that point to the old permalinks, and to communicate with the audience and the sources about the changes.
Fix any technical issues or errors
The first and most important strategy to recover from the traffic loss is to fix any technical issues or errors that might have occurred during the permalink change, such as broken links, missing redirects, duplicate content, or canonical problems. These issues can negatively affect your site’s SEO and user experience, as they can prevent search engines and visitors from finding and accessing your content, and can cause confusion and frustration.
To fix these issues, you need to use the site crawler and the site audit features that we mentioned in the previous section, and follow the recommendations and suggestions that they provide. For example, you can use Screaming Frog or Sitebulb to find and fix any broken links, missing redirects, duplicate content, or canonical problems on your site, and to monitor the results.
Here are some examples of how to fix some common technical issues or errors that might occur during the permalink change:
Broken links: Broken links are links that point to pages that no longer exist or have moved to a different URL. They can cause 404 (Not Found) errors, which can harm your site’s SEO and user experience. To fix broken links, you need to either update them to point to the new URLs, or remove them if they are no longer relevant. You can use Screaming Frog or Sitebulb to find and fix broken links on your site, and to see the list of pages that contain them.
Missing redirects: Missing redirects are pages that have changed their URLs, but have not implemented a redirect to the new URLs. They can cause 404 (Not Found) errors, which can harm your site’s SEO and user experience. To fix missing redirects, you need to implement a 301 (Moved Permanently) redirect from the old URLs to the new URLs, so that search engines and visitors can find and access your content under the new URLs.
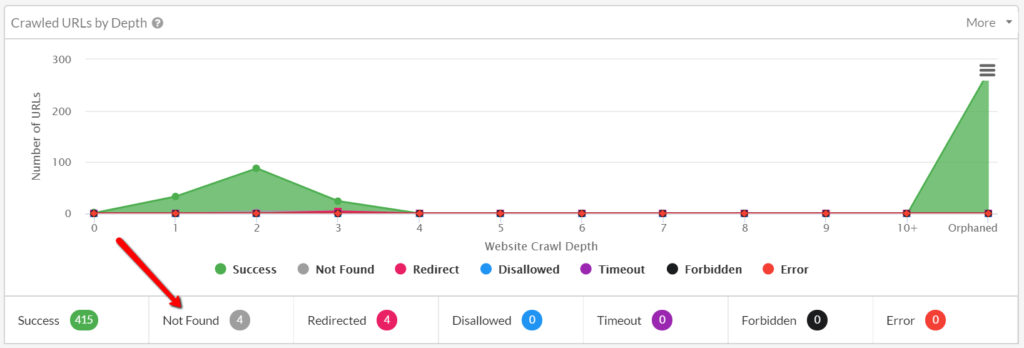
Duplicate content: Duplicate content is content that appears on more than one URL on your site or on other sites. It can harm your site’s SEO and user experience, as it can confuse search engines and visitors about which URL is the original and authoritative source of the content. To fix duplicate content, you need to either consolidate the content to one URL, or use canonical tags to indicate the preferred URL for the content.
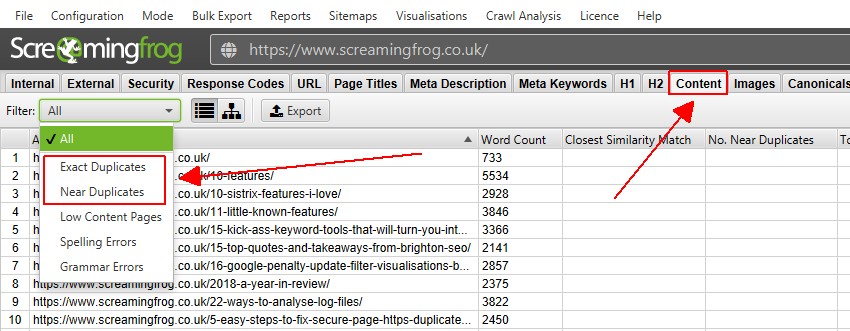
This screenshot shows the duplicate content feature in Screaming Frog, showing the list of duplicate content and the pages that have it. You can see that some of the pages have the same content under different URLs, and that they need to be consolidated or canonicalized.
Canonical problems: Canonical problems are issues that arise when you have more than one URL for the same content, and you have not specified the canonical URL for the content. They can harm your site’s SEO and user experience, as they can cause duplicate content, indexation, and ranking issues. To fix canonical problems, you need to use canonical tags to tell search engines and visitors which URL is the original and authoritative source of the content.
Use redirects, resubmissions, and sitemaps
The second strategy to recover from the traffic loss is to use redirects, resubmissions, and sitemaps to ensure that the new permalinks are properly indexed and crawled by search engines. These techniques can help you to inform search engines about the changes on your site, and to speed up the process of updating their databases and algorithms.
To use these techniques, you need to use Google Search Console and other tools to implement and monitor the results. For example, you can use Google Search Console to create and submit sitemaps, to request indexing for the new permalinks, and to see the status and errors of the redirects and the sitemaps.
Here are some examples of how to use redirects, resubmissions, and sitemaps to recover from the traffic loss:
Redirects: Redirects are instructions that tell search engines and visitors that a page has moved to a different URL, and to automatically redirect them to the new URL. They can help you to preserve the authority and trust that you have built with the old URLs, and to avoid 404 (Not Found) errors. To use redirects, you need to implement a 301 (Moved Permanently) redirect from the old URLs to the new URLs, and to monitor the status and errors of the redirects in Google Search Console.
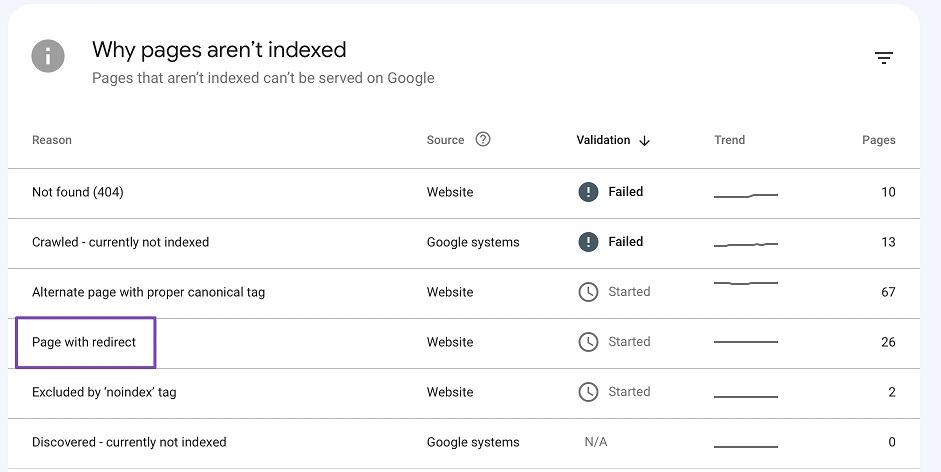
This screenshot shows the redirects feature in Google Search Console, showing the list of redirects and the status and errors of them. You can see that some of the redirects are valid and successful, and some of them have errors or warnings, such as redirect loops, redirect chains, or soft 404s.
Resubmissions: Resubmissions are requests that tell search engines to index and crawl a specific URL or a group of URLs on your site. They can help you to speed up the process of updating the search engines’ databases and algorithms with the new permalinks, and to improve the visibility and rankings of your site. To use resubmissions, you need to request indexing for the new permalinks in Google Search Console, and to monitor the status and errors of the requests.
Sitemaps: Sitemaps are files that list the URLs and other information of your site, such as the last modified date, the priority, and the frequency of change. They can help you to tell search engines about the structure and content of your site, and to make it easier for them to index and crawl your site. To use sitemaps, you need to create and submit sitemaps for the new permalinks in Google Search Console, and to monitor the status and errors of the sitemaps.
Update any internal and external links
The third strategy to recover from the traffic loss is to update any internal and external links that point to the old permalinks, and to communicate with the audience and the sources about the changes. These techniques can help you to improve the SEO and user experience of your site, as they can prevent broken links, redirect loops, and confusion among the visitors and the sources.
To use these techniques, you need to use various tools and methods to find and update the links, and to reach out to the audience and the sources. For example, you can use Screaming Frog or Sitebulb to find and update the internal links on your site, and use tools like Ahrefs or Moz to find and update the external links from other sites. You can also use email, social media, or blog posts to inform the audience and the sources about the permalink change, and to ask them to update the links if possible.
Here are some examples of how to update any internal and external links and communicate with the audience and the sources:
Internal links: Internal links are links that point to other pages on your site. They can help you to improve the SEO and user experience of your site, as they can create a clear and logical site structure, enhance the navigation and usability, and distribute the authority and trust among the pages. To update internal links, you need to find and replace the old permalinks with the new permalinks on your site, and to check the status and errors of the links.
External links: External links are links that point to your site from other sites. They can help you to improve the SEO and user experience of your site, as they can increase the visibility and credibility of your site, drive referral traffic, and build relationships with other sites. To update external links, you need to find and contact the sources that link to your site, and to ask them to update the links to the new permalinks if possible. You can use tools like Ahrefs or Moz to find and contact the sources that link to your site, and to see the list of pages that have the links.
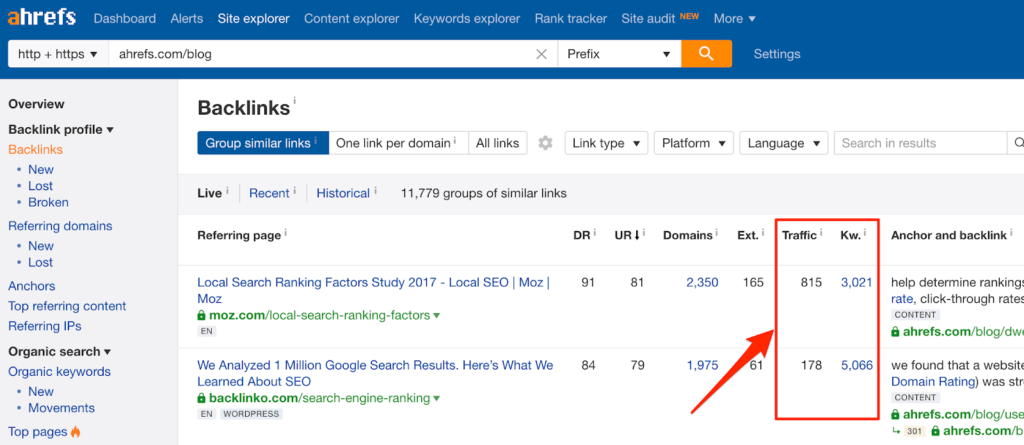
This screenshot shows the external links feature in Ahrefs, showing the list of external links and the pages that have them. You can see that some of the links point to the old permalinks, and that they need to be updated to the new permalinks.
Communication: Communication is the process of informing and engaging with the audience and the sources about the permalink change, and to explain the reasons and benefits of the change. It can help you to improve the SEO and user experience of your site, as it can prevent confusion and frustration among the visitors and the sources, and to increase the trust and loyalty of the audience.
To communicate with the audience and the sources, you need to use email, social media, or blog posts to announce the permalink change, and to provide the new permalinks and any other relevant information. You can also use tools like Mailchimp or Buffer to create and send email or social media campaigns, and to monitor the results.
How to optimize the new permalinks for SEO and user experience
The final step to deal with the permalink change is to optimize the new permalinks for SEO and user experience. This step can help you to take advantage of the permalink change, and to improve the performance and health of your site in the long run. You can use various strategies and methods to optimize the new permalinks for SEO and user experience, such as making the URLs more descriptive, relevant, consistent, and easy to remember, aligning the content with the new site structure, keywords, and goals, and creating a personal brand and standing out from the crowd.
Make the URLs more descriptive, relevant, consistent, and easy to remember
One of the main benefits of changing permalinks is that you can make the URLs more descriptive, relevant, consistent, and easy to remember. This can improve the SEO and user experience of your site, as it can help search engines and visitors to understand what your content is about, how it is organized, and how to access it.
To make the URLs more descriptive, relevant, consistent, and easy to remember, you need to use clear and meaningful words that describe the content and the purpose of the page, and to avoid using unnecessary or confusing words, such as numbers, dates, symbols, or stop words. You also need to use a consistent and logical structure for the URLs, and to follow the best practices and conventions for the URL format, such as using hyphens to separate words, using lowercase letters, and using a trailing slash.
Here are some examples of how to make the URLs more descriptive, relevant, consistent, and easy to remember:
– Bad URL: https://example.com/p=123
– Good URL: https://example.com/how-to-change-permalinks
– Bad URL: https://example.com/2023/04/14/why-changing-permalinks-can-be-good-for-your-site-even-if-you-lose-some-traffic
– Good URL: https://example.com/why-changing-permalinks-can-be-good
– Bad URL: https://example.com/SEO_Tips&Tricks
– Good URL: https://example.com/seo-tips-and-tricks/
Align the content with the new site structure, keywords, and goals
Another benefit of changing permalinks is that you can align the content with the new site structure, keywords, and goals. This can improve the SEO and user experience of your site, as it can help you to revamp your content strategy and attract new visitors, by creating and delivering content that matches the expectations and needs of your audience and the search engines.
To align the content with the new site structure, keywords, and goals, you need to review and update your content according to the new permalinks, and to make sure that the content is relevant, useful, engaging, and optimized for the target keywords and the search intent. You also need to use a clear and logical site structure, and to use headings, subheadings, lists, and other formatting elements to organize and present your content in a user-friendly and search-friendly way.
Here are some examples of how to align the content with the new site structure, keywords, and goals:
Old content: How to Change Permalinks in WordPress (And Why You Should Do It)
New content: Why Changing Permalinks Can Be Good For Your Site (Even If You Lose Some Traffic)
Old content: Permalinks are the permanent URLs of your web pages and posts. They are one of the most important factors for SEO and user experience, as they tell search engines and visitors what your content is about, how it is organized, and how to access it. In this article, we will show you how to change permalinks in WordPress, and why you should do it.
New content: Permalinks are the permanent URLs of your web pages and posts. They are one of the most important factors for SEO and user experience, as they tell search engines and visitors what your content is about, how it is organized, and how to access it. However, sometimes you might need or want to change your permalinks, either intentionally or unintentionally. This can happen due to various reasons, such as human error, plugin updates, or server issues. Changing permalinks can have a significant impact on your site, as it can cause a temporary drop in organic traffic and rankings. But don’t panic! Changing permalinks can also be beneficial for your site in the long run, and the traffic loss can be embraced as a natural consequence of improving your site. In this article, we will show you how to assess the impact of the permalink change, how to recover from the traffic loss, and how to optimize the new permalinks for SEO and user experience.
Create a personal brand and stand out from the crowd
The final benefit of changing permalinks is that you can create a personal brand and stand out from the crowd. This can improve the SEO and user experience of your site, as it can help you to convey the unique value proposition and personality of your site, and to differentiate yourself from the competitors and the noise.
To create a personal brand and stand out from the crowd, you need to use permalinks to express your voice, style, and tone, and to communicate your mission, vision, and values. You also need to use permalinks to showcase your expertise, authority, and trustworthiness, and to build relationships with your audience and the sources. You can also use permalinks to create a memorable and recognizable identity for your site, and to encourage loyalty and advocacy among your visitors and the sources.
Here are some examples of how to create a personal brand and stand out from the crowd:
Generic URL: https://example.com/how-to-write-a-blog-post
Personal URL: https://example.com/how-i-write-killer-blog-posts
Generic URL: https://example.com/seo-guide
Personal URL: https://example.com/seo-secrets-from-a-pro
Generic URL: https://example.com/about
Personal URL: https://example.com/my-story
Conclusion
In conclusion, changing permalinks can be good for your site, even if you lose some traffic in the short term. Changing permalinks can help you to improve the SEO and user experience of your site, by making the URLs more descriptive, relevant, consistent, and easy to remember, aligning the content with the new site structure, keywords, and goals, and creating a personal brand and standing out from the crowd.
However, changing permalinks can also have a significant impact on your site, as it can cause a temporary drop in organic traffic and rankings. To deal with the permalink change, you need to assess the impact of the permalink change, recover from the traffic loss, and optimize the new permalinks for SEO and user experience.
We hope that this article has helped you to understand the pros and cons of changing permalinks, and how to do it effectively and efficiently. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to leave them below. We would love to hear from you and help you with your permalink change. Thank you for reading and happy blogging!
– “Permalinks are the permanent URLs to your individual pages and blog posts, as well as your category and tag archives. A permalink is the web address used to link to your content. The permalink is the full URL you see – and use – for any given post, page or other pieces of content on your site. It’s a permanent link, hence the name permalink.” – [Yoast]
– “Changing your permalinks can have a negative impact on your site’s SEO performance, especially if you don’t do it correctly. If you change the URL of a page, Google will treat it as a new page and it will lose all the SEO value it had before. That’s why you need to use 301 redirects to tell Google that the old URL has moved to the new one, and transfer the SEO value to the new page.” – [WPBeginner]
– “Changing your permalinks can also have a positive impact on your site’s SEO performance, if you do it for the right reasons and in the right way. For example, if you change your permalinks to make them more descriptive, relevant, and user-friendly, you can improve your click-through rate, your bounce rate, and your dwell time, which are all ranking factors. You can also optimize your permalinks for your target keywords, and make them more consistent with your site structure and content.” – [Neil Patel]