Problems are inevitable in life and work. No matter how much we plan ahead or anticipate the challenges, we will always encounter some difficulties that require our attention and action.
Therefore, problem solving is a crucial skill for managers and leaders who need to deal with problems in their everyday tasks and projects.
In this article, we will explore what problems are, how to identify and analyze them, and what tools and techniques we can use to solve them or mitigate their impact.
What is a Problem?
A problem is a gap between what is expected and what is happening. It is a situation that causes dissatisfaction, frustration, or difficulty for someone.
A problem can be simple or complex, depending on the nature, scope, and impact of the issue. A problem can also be well-defined or ill-defined, depending on the clarity, availability, and reliability of the information about the issue.
How to Identify and Analyze Problems?

Before we can solve a problem, we need to understand it. This involves identifying the problem, defining its scope and boundaries, and analyzing its causes and effects. Some steps that can help us in this process are:
- Step I: What should happen? This is the desired state or goal that we want to achieve. It can be based on our plans, expectations, experiences, intuitions, or social norms. We need to be clear and specific about what we want to happen and why.
- Step II: What is happening? This is the current state or reality that we are facing. It can be based on our observations, measurements, data, or feedback. We need to be accurate and objective about what is happening and how.
- Step III: Why is it happening? This is the root cause or reason behind the problem. It can be based on our analysis, logic, evidence, or assumptions. We need to be thorough and systematic about why it is happening and what factors are influencing it.
- Step IV: Prioritizing the causes of the problem. This is the ranking or ordering of the causes based on their importance, urgency, or feasibility. It can be based on our criteria, standards, or preferences. We need to be realistic and pragmatic about which causes are more relevant, critical, or solvable.
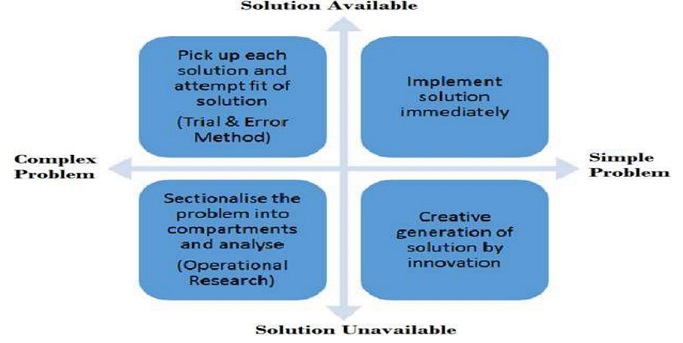
How to Solve Problems?
Once we have identified and analyzed the problem, we can move on to finding and implementing solutions. This involves generating, evaluating, and selecting alternatives, and then executing, monitoring, and reviewing the results. Some steps that can help us in this process are:
- Step V: What should be done? Finding solutions to the causes. This is the generation and evaluation of possible solutions that can address the causes of the problem. It can be based on our creativity, knowledge, experience, or research. We need to be innovative and diverse about what can be done and how.
- Step VI: What has been done? Applying the solution to solve the problem. This is the selection and implementation of the best solution that can solve the problem. It can be based on our criteria, resources, constraints, or risks. We need to be decisive and effective about what has been done and how.
What Tools and Techniques Can We Use to Solve Problems?
There are many tools and techniques that can help us in the problem solving process. Some of them are:
- DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control): This is a structured and data-driven methodology that can be used to improve the quality and performance of a process or product. It involves defining the problem and the goal, measuring the current state and the gap, analyzing the root causes and the factors, improving the process or product by implementing solutions, and controlling the results by monitoring and sustaining the improvement.
- PDCA (Plan, Do, Check, Act): This is a simple and iterative cycle that can be used to test and implement changes in a process or product. It involves planning the change and the expected outcome, doing the change and collecting data, checking the data and the outcome, and acting on the results by standardizing or modifying the change.
- Operations Research: This is a scientific and mathematical approach that can be used to provide a quantitative basis for complex and uncertain managerial decisions. It involves formulating the problem as a mathematical model, solving the model using various techniques, and interpreting and implementing the solution in the real world.
- DECIDE Model: This is a logical and rational technique that can be used to make a more informed and effective decision. It involves detecting the change or the need for a decision, estimating the significance and the impact of the change, choosing the desired outcome and the criteria, identifying the options and the alternatives, doing the best option and the action, and evaluating the results and the feedback.
- Rule of 6 C’s of Decision Making: This is a checklist that can be used to ensure a comprehensive and consistent decision making process. It involves constructing a clear picture of what needs to be done, compiling a list of requirements and constraints, collecting information on alternatives and options, comparing alternatives and options based on criteria and trade-offs, considering what might go wrong and the risks and uncertainties, and committing to the action and the implementation.
Final Thoughts
Problem solving is an essential skill for managers and leaders who need to deal with problems in their everyday life and work. Problem solving is not a one-size-fits-all solution, but rather an individual and situational skill that varies from person to person and from problem to problem.
Therefore, we need to be flexible and adaptable in applying different tools and techniques to different problems, and learn from our experiences and feedback. By doing so, we can improve our problem solving ability and achieve our goals more effectively and efficiently.
The Problems and Pitfalls of Google’s Helpful Content Update
What Company Departments Are Most Useful For Solving People’s Problems